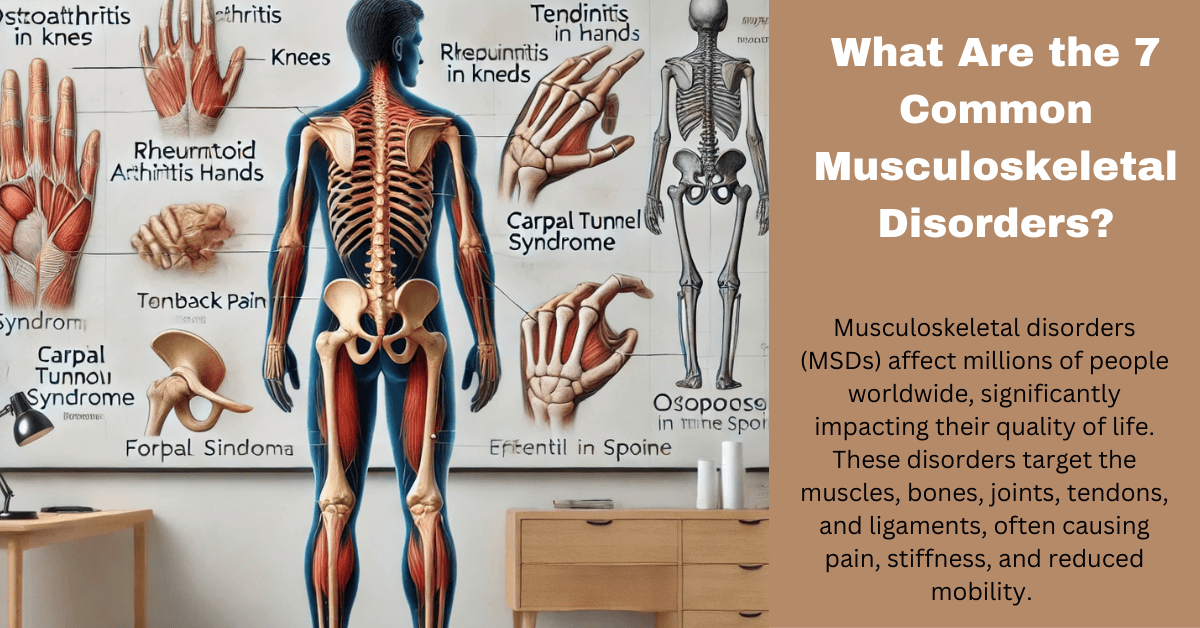
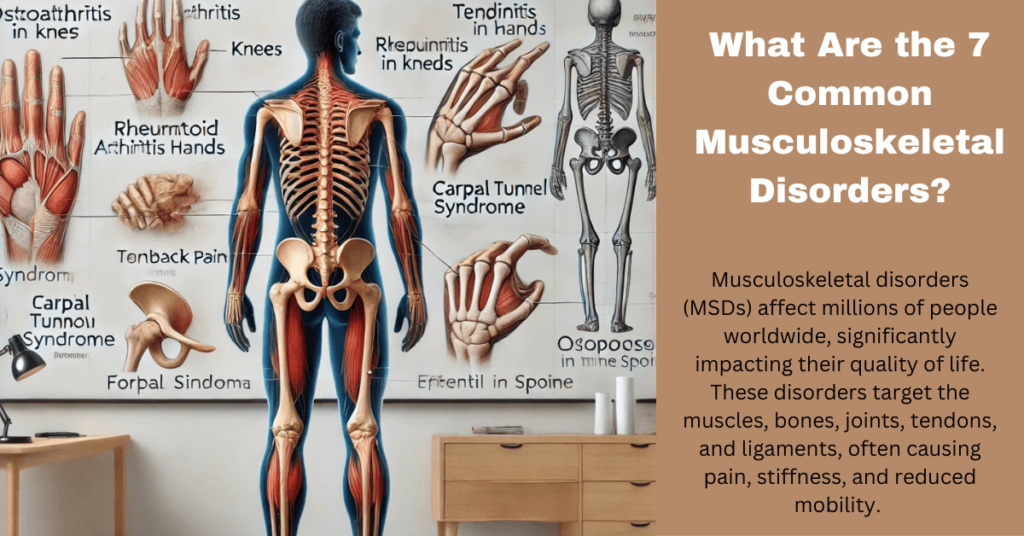
What Are the 7 Common Musculoskeletal Disorders? A Comprehensive Guide Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) affect millions of people worldwide, significantly impacting their quality of life. These disorders target the muscles, bones, joints, tendons, and ligaments, often causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Understanding the most prevalent musculoskeletal disorders can help in early diagnosis and effective management. This article explores what are the 7 common musculoskeletal disorders, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
1. Osteoarthritis: The Wear-and-Tear Disease
Osteoarthritis is one of the most widespread musculoskeletal disorders, affecting the cartilage that cushions joints.
Key Features:
- Causes: Age-related wear and tear, obesity, joint injuries, or genetic predisposition.
- Symptoms: Joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion.
- Commonly Affected Areas: Knees, hips, hands, and spine.
Management Tips:
- Regular low-impact exercise like swimming or walking.
- Use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief.
- Physical therapy to improve joint function.
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Autoimmune Challenge
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues.
Key Features:
- Causes: Genetic factors, environmental triggers, and hormonal imbalances.
- Symptoms: Persistent joint inflammation, fatigue, fever, and morning stiffness.
- Commonly Affected Areas: Hands, wrists, knees, and feet.
Management Tips:
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) to slow disease progression.
- Biologic therapies targeting specific immune responses.
- Regular exercise and a balanced diet to reduce inflammation.
3. Low Back Pain: A Universal Complaint
Low back pain is among the most common musculoskeletal disorders, often linked to lifestyle factors or underlying conditions.
Key Features:
- Causes: Poor posture, herniated discs, muscle strains, or degenerative disc disease.
- Symptoms: Pain in the lower back, muscle spasms, and difficulty standing or walking.
- Commonly Affected Areas: Lumbar spine region.
Management Tips:
- Core-strengthening exercises to support the spine.
- Heat or cold therapy to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Ergonomic adjustments in the workplace and home.
4. Tendinitis: Overuse Injuries at Their Peak
Tendinitis refers to the inflammation of tendons, typically resulting from repetitive strain or overuse.
Key Features:
- Causes: Repetitive activities, sudden injuries, or poor posture.
- Symptoms: Pain, tenderness, and swelling near the affected tendon.
- Commonly Affected Areas: Shoulders (rotator cuff tendinitis), elbows (tennis elbow), knees, and wrists.
Management Tips:
- Rest and avoid activities that exacerbate the condition.
- Apply ice to reduce swelling and pain.
- Physical therapy to restore strength and flexibility.
5. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Modern-Day Epidemic
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a nerve-related musculoskeletal disorder caused by compression of the median nerve in the wrist.
Key Features:
- Causes: Repetitive hand movements, wrist injuries, or conditions like diabetes.
- Symptoms: Numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain in the hand and fingers.
- Commonly Affected Areas: Wrist and hand.
Management Tips:
- Use ergonomic tools to reduce wrist strain.
- Wear wrist splints, especially at night.
- In severe cases, surgery may be required to relieve nerve pressure.
6. Fibromyalgia: Chronic Pain Amplified
Fibromyalgia is a complex musculoskeletal disorder characterized by widespread pain and heightened pain sensitivity.
Key Features:
- Causes: Unknown, but linked to genetic, psychological, and environmental factors.
- Symptoms: Muscle pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and cognitive issues (often called “fibro fog”).
- Commonly Affected Areas: Entire body, especially the neck, shoulders, back, and hips.
Management Tips:
- Regular physical activity, such as yoga or tai chi.
- Medications like pain relievers or antidepressants.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to manage symptoms.
7. Osteoporosis: The Silent Bone Thief
Osteoporosis is a musculoskeletal condition that weakens bones, making them more prone to fractures.
Key Features:
- Causes: Aging, hormonal changes, vitamin D deficiency, or a sedentary lifestyle.
- Symptoms: Often asymptomatic until a fracture occurs; back pain and a hunched posture may develop over time.
- Commonly Affected Areas: Spine, hips, and wrists.
Management Tips:
- Calcium and vitamin D supplementation.
- Weight-bearing exercises like walking or resistance training.
- Medications like bisphosphonates to strengthen bone density.
How to Prevent Musculoskeletal Disorders
While some MSDs are inevitable due to genetic factors or aging, others can be prevented with proactive measures:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reducing stress on joints and muscles.
- Stay Active: Engage in regular exercise to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
- Practice Good Posture: Avoid slouching, especially during prolonged sitting or standing.
- Use Ergonomic Equipment: Adapt your workspace to reduce strain on muscles and joints.
- Listen to Your Body: Address early signs of pain or stiffness before they worsen.
When to Seek Professional Help
While self-care and lifestyle changes can manage many musculoskeletal disorders, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider if:
- Pain or stiffness persists for more than a week.
- Symptoms worsen or interfere with daily activities.
- You experience swelling, redness, or loss of mobility.
- You have a history of fractures or family predisposition to musculoskeletal conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding what are the 7 common musculoskeletal disorders is the first step toward prevention and effective management. From osteoarthritis to osteoporosis, each condition presents unique challenges but also opportunities for proactive care. By staying informed, adopting healthy habits, and seeking timely medical intervention, you can protect your musculoskeletal health and maintain an active, pain-free life.