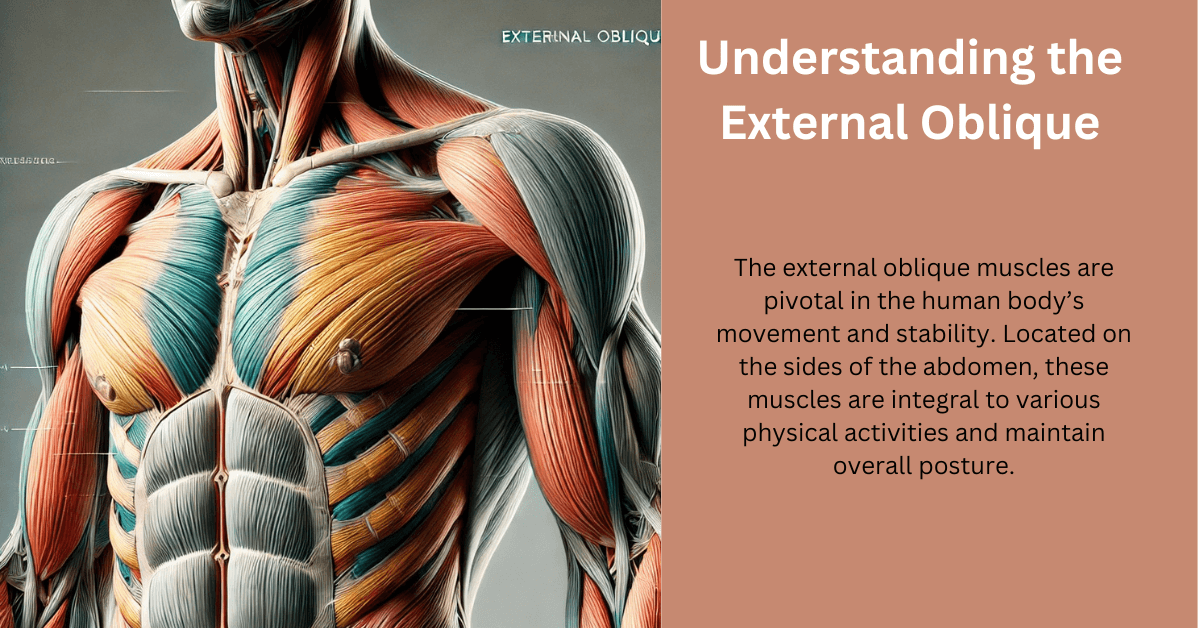
Understanding the External Oblique: A Vital Component of Core Strength. The external oblique muscles are pivotal in the human body’s movement and stability. Located on the sides of the abdomen, these muscles are integral to various physical activities and maintain overall posture. In this article, we delve into the main function of the external oblique, its anatomical significance, and how to keep it healthy and strong.
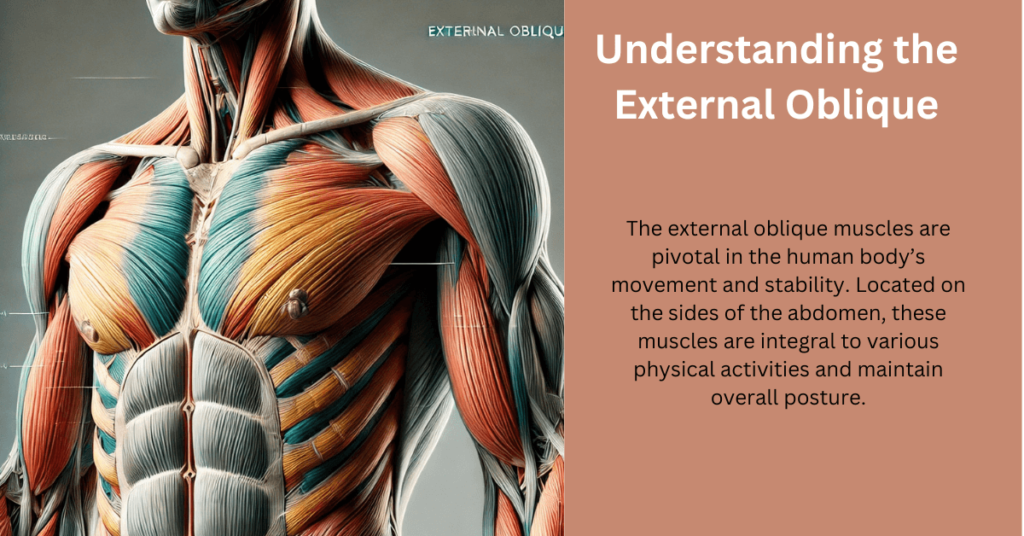
Anatomy of the External Oblique
To fully comprehend the main function of the external oblique, it’s crucial to understand its anatomical structure. The external oblique is one of the largest abdominal muscles, positioned superficially on either side of the torso. It originates from the lower eight ribs and inserts into the iliac crest and linea alba. Its fibers run diagonally downward and medially, forming a characteristic V-shape. This unique alignment allows the external oblique to perform various critical movements and contribute to core stability.
What is the Main Function of the External Oblique?
The primary role of the external oblique is to facilitate movement and maintain stability. Here are the main functions:
- Trunk Rotation: The external oblique is heavily involved in twisting or rotating the torso. This action is essential for movements such as turning to look over your shoulder or performing a golf swing.
- Lateral Flexion: This muscle enables side-bending motions, allowing you to tilt your body to the left or right.
- Compression of Abdominal Contents: The external oblique helps compress the abdomen, assisting in functions like forced exhalation, coughing, and childbirth.
- Postural Stability: Alongside other core muscles, the external oblique supports the spine and pelvis, ensuring proper alignment and balance during daily activities.
By fulfilling these functions, the external oblique contributes significantly to both dynamic movements and static postures.
Importance of a Strong External Oblique
A robust external oblique muscle is crucial for overall physical health. Its strength and functionality directly influence athletic performance, injury prevention, and daily life activities. Below are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Athletic Performance: Sports that involve rotational movements, such as tennis, baseball, and swimming, rely heavily on the external oblique. Strengthening this muscle improves speed, agility, and power.
- Reduced Risk of Injury: Weak external obliques can lead to imbalances in the core, increasing the likelihood of injuries like lower back pain or muscle strains.
- Improved Posture: A strong external oblique supports spinal alignment, reducing slouching and promoting a healthy stance.
- Core Coordination: As part of the abdominal muscle group, the external oblique works in tandem with other muscles to enhance overall core stability.
Exercises to Strengthen the External Oblique
Incorporating targeted exercises into your fitness routine can significantly improve the strength and functionality of the external oblique. Here are some effective exercises:
- Side Planks: This static hold strengthens the obliques by engaging them to maintain balance.
- Russian Twists: Sitting with your feet off the ground, twist your torso side to side while holding a weight or medicine ball.
- Bicycle Crunches: Lying on your back, alternate bringing your elbow to the opposite knee in a pedaling motion.
- Woodchoppers: Using a cable machine or resistance band, mimic a chopping motion, moving diagonally across your body.
- Oblique V-Ups: Lying on one side, lift both your upper body and legs simultaneously toward each other.
Consistency in performing these exercises can lead to noticeable improvements in strength and flexibility.
External Oblique and Everyday Activities
The main function of the external oblique extends beyond fitness; it plays a vital role in daily life. From bending down to pick up an object to twisting while driving, the external oblique is constantly at work. Understanding its function emphasizes the importance of maintaining its health to perform these tasks efficiently.
Additionally, the external oblique’s role in stabilizing the core is critical for preventing falls and maintaining balance, particularly in older adults. Strengthening this muscle can enhance functional independence and overall quality of life.
Common Issues and Injuries
Like any other muscle, the external oblique is susceptible to strains and injuries, especially during sudden movements or overuse. Common issues include:
- Muscle Strains: Overstretching or tearing of the muscle fibers can result in pain and limited movement.
- Imbalances: Weak or underactive obliques can lead to poor posture and compensatory movement patterns.
- Overuse Injuries: Repeated stress on the external oblique, often seen in athletes, can cause inflammation or discomfort.
Preventing these issues involves proper warm-ups, gradual progression in exercise intensity, and maintaining balanced strength across all core muscles.
Stretching and Recovery
To maintain the flexibility and health of the external oblique, regular stretching is essential. Here are a few effective stretches:
- Seated Side Stretch: Sit cross-legged, extend one arm overhead, and lean to the opposite side.
- Standing Side Bend: Stand tall, place one hand on your hip, and reach the other arm overhead, bending to the side.
- Twisting Stretch: Sit on the floor, cross one leg over the other, and twist your torso toward the bent knee.
Incorporating these stretches into your routine can improve muscle elasticity and reduce the risk of injuries.
Nutrition for Muscle Health
Optimal nutrition plays a vital role in supporting the health and function of the external oblique. Ensure your diet includes:
- Protein: Promotes muscle repair and growth.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Reduces inflammation and aids recovery.
- Antioxidants: Protect muscles from oxidative stress.
- Electrolytes: Maintains hydration and prevents cramps.
Staying hydrated and consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients will keep your external oblique and other muscles functioning at their best.
The Role of the External Oblique in Breathing
An often-overlooked function of the external oblique is its contribution to respiration. During forced exhalation, such as coughing or heavy breathing, the external oblique contracts to push air out of the lungs. This highlights its importance in respiratory efficiency and overall health.
Conclusion
The external oblique is a cornerstone of core strength and functional movement. Understanding its main function—from enabling trunk rotation to stabilizing posture—underscores its significance in both fitness and daily activities. By prioritizing exercises, stretches, and proper nutrition, you can ensure your external oblique remains strong and resilient. Embrace the benefits of a well-conditioned external oblique to enhance your physical performance and overall well-being.