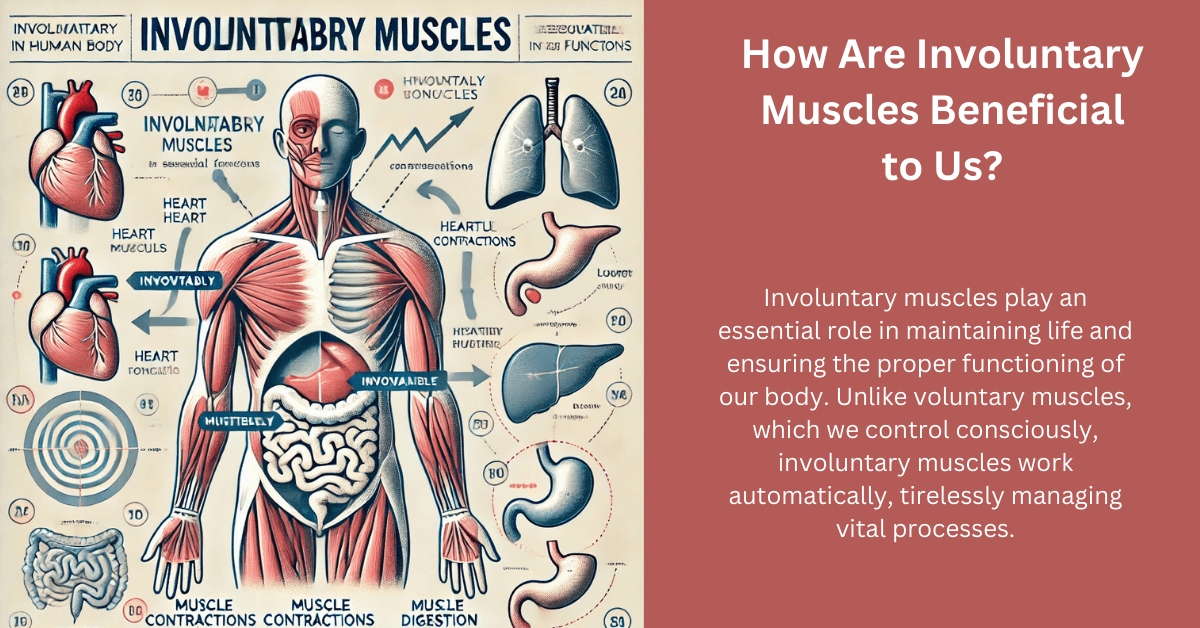
How Are Involuntary Muscles Beneficial to Us? Understanding Their Crucial Role in the Body. Involuntary muscles play an essential role in maintaining life and ensuring the proper functioning of our body. Unlike voluntary muscles, which we control consciously, involuntary muscles work automatically, tirelessly managing vital processes. But how are involuntary muscles beneficial to us? This article dives deep into their functions, types, and the incredible ways they support our health and well-being.
What Are Involuntary Muscles?
Involuntary muscles are muscles that function without conscious control. They are regulated by the autonomic nervous system and play a key role in various bodily functions. There are two main types of involuntary muscles:
- Smooth Muscles:
- Found in the walls of internal organs like the stomach, intestines, blood vessels, and bladder.
- Responsible for processes like digestion, circulation, and excretion.
- Cardiac Muscles:
- Found exclusively in the heart.
- Pump blood throughout the body, ensuring oxygen and nutrient delivery.
Both types of involuntary muscles are crucial to our survival and operate continuously without our awareness.
The Vital Benefits of Involuntary Muscles
Involuntary muscles perform a wide range of functions that are indispensable to life. Let’s explore how involuntary muscles are beneficial to us:
1. Facilitating Blood Circulation
- Role of Cardiac Muscles:
- The heart, made up of cardiac muscle, beats rhythmically to pump blood throughout the body.
- It ensures that oxygen-rich blood reaches tissues and organs while removing carbon dioxide and waste products.
- Smooth Muscles in Blood Vessels:
- Smooth muscles in the walls of arteries and veins regulate blood pressure by contracting and relaxing.
- This helps maintain proper blood flow, even during changes in posture or activity levels.
2. Supporting the Digestive System
- Peristalsis:
- Smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract move food along through a process called peristalsis.
- These rhythmic contractions ensure the efficient digestion and absorption of nutrients.
- Sphincter Control:
- Smooth muscles control sphincters, which regulate the passage of food and waste within the digestive system.
3. Regulating Breathing
- Involuntary Control of Diaphragm:
- The diaphragm and intercostal muscles, though partly voluntary, function involuntarily to enable breathing.
- These muscles contract and relax to draw air into the lungs and expel carbon dioxide, ensuring consistent oxygen supply.
4. Maintaining Homeostasis
- Thermoregulation:
- Smooth muscles in blood vessels help regulate body temperature by constricting or dilating to retain or release heat.
- Bladder Control:
- Smooth muscles in the urinary system store and release urine, maintaining fluid balance and waste elimination.
5. Enabling Childbirth
- Role in Labor:
- During childbirth, smooth muscles in the uterus contract rhythmically to help deliver the baby.
- These contractions, regulated by hormones, are a crucial aspect of labor.
6. Supporting Vision
- Iris and Pupil Adjustment:
- Smooth muscles in the eye control the size of the pupil, adjusting to changes in light intensity.
- This automatic adjustment protects the retina and ensures clear vision.
How Involuntary Muscles Work Behind the Scenes
Involuntary muscles operate under the control of the autonomic nervous system, which has two branches:
- Sympathetic Nervous System:
- Prepares the body for “fight or flight” responses by increasing heart rate, dilating airways, and constricting blood vessels.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System:
- Promotes “rest and digest” activities, slowing the heart rate, enhancing digestion, and relaxing blood vessels.
The seamless coordination of these systems ensures that involuntary muscles respond appropriately to the body’s needs.
Examples of Daily Activities Involuntary Muscles Manage
- Digesting Breakfast:
- Smooth muscles in the stomach and intestines process food while you focus on other tasks.
- Walking to Work:
- Cardiac muscles ensure steady blood circulation to fuel your muscles and brain.
- Relaxing in the Evening:
- Smooth muscles adjust blood flow and help you recover from the day’s activities.
Disorders Related to Involuntary Muscles
While involuntary muscles are vital, issues can arise that affect their function, such as:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
- Abnormal contractions of smooth muscles in the intestines cause discomfort and digestive issues.
- Hypertension:
- Excessive contraction of smooth muscles in blood vessels increases blood pressure.
- Arrhythmia:
- Irregular heartbeats caused by malfunctions in cardiac muscles.
- Asthma:
- Overactivity of smooth muscles in the airways leads to breathing difficulties.
How to Keep Involuntary Muscles Healthy
To ensure the optimal functioning of involuntary muscles, adopt these habits:
- Maintain a Balanced Diet:
- Consume nutrient-rich foods to support muscle and nerve health.
- Stay Active:
- Regular exercise improves blood circulation and strengthens the cardiovascular system.
- Manage Stress:
- Chronic stress can affect the autonomic nervous system and disrupt muscle function.
- Avoid Smoking and Excess Alcohol:
- These habits harm blood vessels and the heart, impairing involuntary muscle health.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Adequate water intake supports smooth muscle function and overall body processes.
Final Thoughts
So, how are involuntary muscles beneficial to us? From powering essential processes like breathing and digestion to regulating blood flow and supporting childbirth, involuntary muscles are indispensable. These unsung heroes work tirelessly behind the scenes, enabling us to live and thrive. By understanding their importance and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, we can ensure these muscles continue to function optimally throughout our lives.